Iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING. 16 thoughts on “ How to monitor Linux servers with SNMP and Cacti ” Reply. Michael Mol on November 29, 2013 at 3:14 pm said. Download Cacti. The latest stable version is 1.1.33, released 01/22/18. Cacti requires MySQL, PHP, RRDTool, net-snmp, and a webserver that supports PHP such as Apache or IIS. Please see the requirements section of the manual for information on how to fulfill these requirements under certain operating systems.
SNMP (or Simple Network Management Protocol) is used to gather data on what is going on within a device, such as load, hard disk states, bandwidth. These data are used by network monitoring tools such as to generate graphs for monitoring purposes. In a typical deployment of Cacti and SNMP, there will be one or more SNMP-enabled devices, and a separate monitoring server where Cacti collects SNMP feeds from those devices. Please keep in mind that all the devices that need to be monitored must be SNMP enabled. In this tutorial, we will be configuring Cacti and SNMP on the same Linux server for demonstration purpose. Configure SNMP on Debian or Ubuntu To install SNMP agent ( snmpd) on a Debian-based system, run the following command. Driver S License Renewal Lto Philippines Traffic Signs. Next, we set the device parameters.
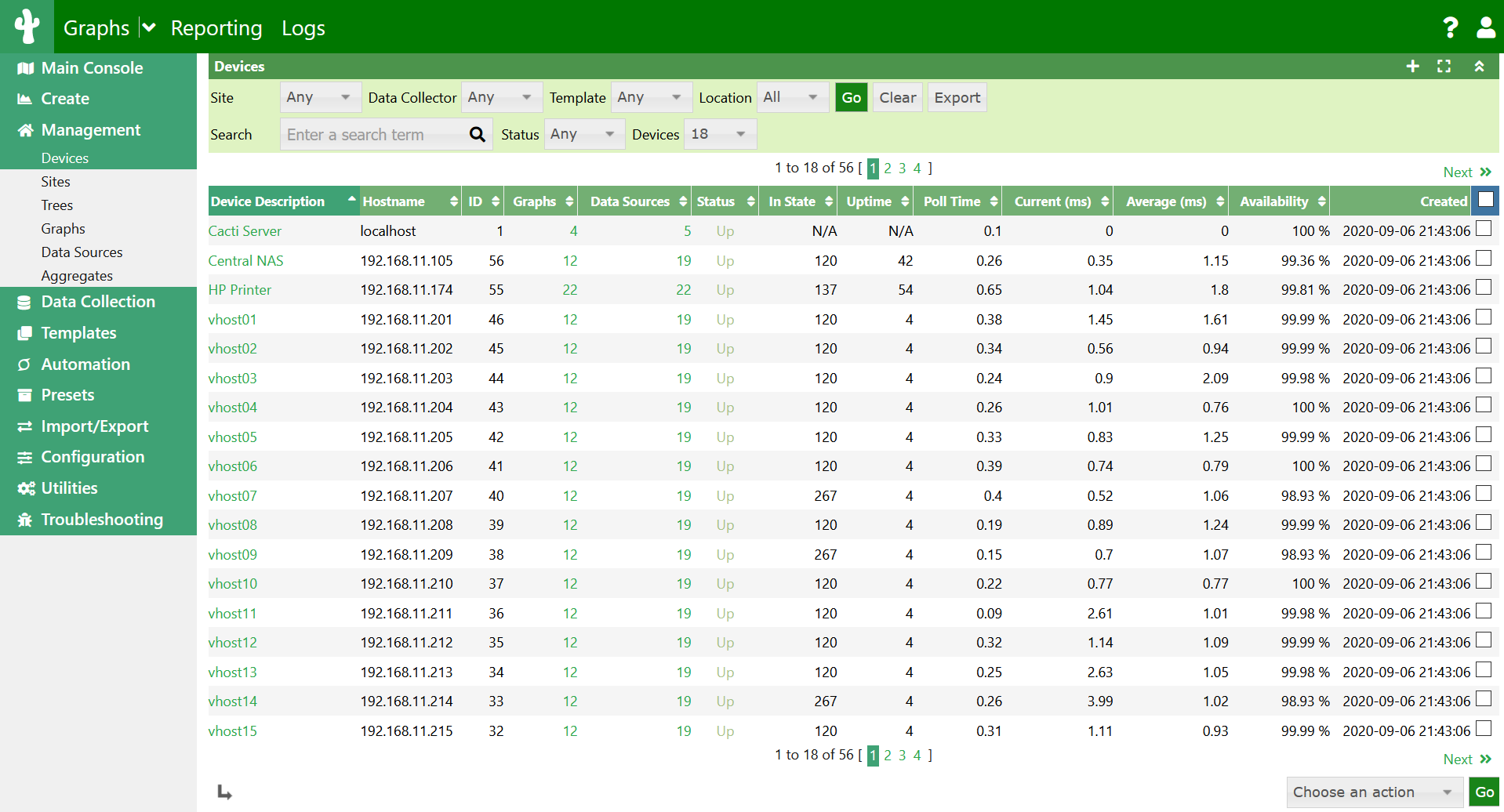
Now that the device has been added, we specify the graph templates that we want to create. This section can be found in the bottom section of the page. And then we proceed to creating the graphs. Here, we create graphs for load average, RAM and hard disk, processor. Interface Graphs and 64-bit Counters By default, Cacti uses 32-bit counters in SNMP queries. 32-bit counters are sufficient for most bandwidth graphs, but they do not work correctly for graphs greater than 100 Mbps.
If it is known that the bandwidth will exceed more than 100 Mbps, it is always advisable to use 64-bit counters. Using 64-bit counters is not hard at all. Note: It takes around 15 minutes for Cacti to populate new graphs. There are not alternatives to being patient. Creating Graph Trees These snapshots illustrate how to create graph trees and how to add graph to those trees.
We can verify the graph in the graph tree. User Management Finally, we create a user with view permission to only the graph that we have created. Cacti has built in user management system, and it is highly customizable. After completing these steps, we can log in with the user 'user1' and verify that only this user is able to view the graph. And thus we have deployed a Cacti server in the network monitoring system. Cacti servers are stable, and can deal with tons of graphs without any problems.
Hope this helps.
Install Cacti in RHEL / CentOS / Fedora In this how-to we are going to show you how to install and setup complete network monitoring application called Cacti using Net-SNMP tool on RHEL 7.x/6.x/5.x, CentOS 7.x/6.x/5.x and Fedora 24-12 systems using YUM and (Fedora 23 onwards) package manager tool. Cacti Required Packages The Cacti required following packages to be installed on your Linux operating systems like RHEL / CentOS / Fedora. • Apache: A Web server to display network graphs created by PHP and RRDTool. • MySQL: A Database server to store cacti information.
• PHP: A script module to create graphs using RRDTool. • PHP-SNMP: A PHP extension for SNMP to access data. • NET-SNMP: A SNMP ( Simple Network Management Protocol) is used to manage network.
• RRDTool: A database tool to manage and retrieve time series data like CPU load, Network Bandwidth etc. Installing Cacti Required Packages on RHEL / CentOS / Fedora First, we need to install following dependency packages one-by-one using YUM package manager tool.
Install Apache # yum install httpd httpd-devel --------- On Fedora 22+ releases --------- # dnf install httpd httpd-devel. Australia Visitor Visa Form 1419 here. MySQL Installation MariaDB is a community-developed fork of the MySQL database project, and provides a replacement for MySQL.
Previously the official supported database was MySQl under RHEL/CentOS 6.x/5.x and Fedora. Recently, RedHat makes a new transaction from MySQl to MariaDB, as MariaDB is the default implementation of MySQL in RHEL/CentOS 7.x and Fedora 19 onwards. # yum install mariadb-server -y [ On RHEL/CentOS 7.x and Fedora 19 onwards] # dnf install mariadb-server -y [ On Fedora 22+ onwards]. Enable Services at Boot Using systemctl Install Cacti on RHEL / CentOS / Fedora Here, you need to install and enable. Once you’ve enabled repository, type the following command to install Cacti application.